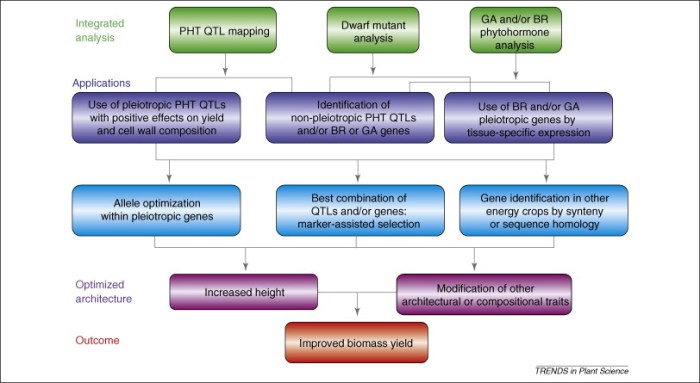
Data nugget growing energy comparing biofuel crop biomass presents a comprehensive analysis of the factors influencing biofuel crop growth, the energy content of various biofuel crops, and the methods used to harvest and process biomass. This exploration unveils the potential of biofuel crops as a sustainable energy source.
The report delves into the environmental and economic benefits of growing biofuel crops, highlighting their role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and diversifying energy sources. It also examines the challenges and opportunities associated with biomass harvesting and processing, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices.
Biofuel Crop Biomass Growth
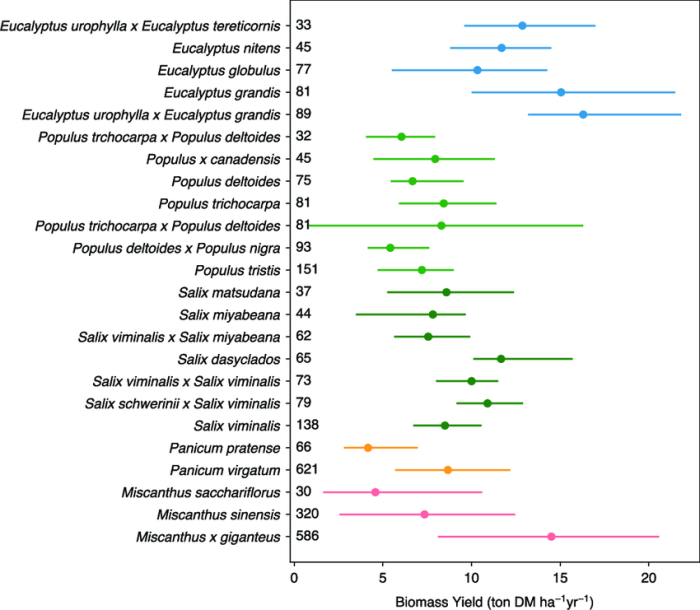
Biofuel crops are plants that are grown specifically for the production of biofuels, which are renewable energy sources derived from biomass. The growth of biofuel crops is influenced by a variety of factors, including climate, soil conditions, and agricultural practices.
The yield and productivity of biofuel crops vary depending on the specific crop and the growing conditions. Some of the most common biofuel crops include corn, soybeans, and sugarcane. Corn is a relatively high-yielding crop that can be grown in a wide range of climates.
Soybeans are also a high-yielding crop, but they require warmer climates. Sugarcane is a tropical crop that is grown primarily for the production of ethanol.
The environmental and economic benefits of growing biofuel crops are significant. Biofuel crops can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and create jobs. They can also help to reduce our dependence on foreign oil.
Comparison of Biofuel Crops
The energy content of different biofuel crops varies depending on the type of crop and the growing conditions. Corn has a relatively high energy content, while soybeans and sugarcane have lower energy contents. The advantages and disadvantages of using different biofuel crops also vary.
Corn is a relatively low-cost crop to grow, and it can be processed into ethanol relatively easily. However, corn production can require a lot of water and fertilizer, and it can contribute to soil erosion. Soybeans are a good source of protein, and they can be processed into biodiesel.
However, soybean production can require a lot of land, and it can contribute to deforestation.
Sugarcane is a high-yielding crop that can be grown in tropical climates. Sugarcane can be processed into ethanol or sugar. However, sugarcane production can require a lot of water and fertilizer, and it can contribute to soil erosion.
The choice of which biofuel crop to grow depends on a variety of factors, including the climate, the soil conditions, and the availability of land and water.
Harvesting and Processing Biomass, Data nugget growing energy comparing biofuel crop biomass
The methods used to harvest and process biomass from biofuel crops vary depending on the specific crop. Corn is typically harvested using a combine, while soybeans are harvested using a combine or a sickle bar mower. Sugarcane is harvested using a sugarcane harvester.
Once the biomass has been harvested, it must be processed into a form that can be used to produce biofuel. Corn is typically processed into ethanol using a dry mill or a wet mill. Soybeans are processed into biodiesel using a transesterification process.
Sugarcane is processed into ethanol using a fermentation process.
The challenges and opportunities associated with biomass harvesting and processing include the cost of harvesting and processing, the environmental impacts of harvesting and processing, and the development of new and more efficient harvesting and processing technologies.
Sustainable biomass management practices are essential to ensure that the production of biofuel crops does not have a negative impact on the environment. Sustainable biomass management practices include using sustainable farming practices, protecting water resources, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Data Analysis and Modeling
| Crop | Yield (tons/acre) | Energy Content (BTU/lb) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 10-15 | 8,000 | High yield, low cost, easy to process | Requires a lot of water and fertilizer, can contribute to soil erosion |
| Soybeans | 50-60 | 10,000 | Good source of protein, can be processed into biodiesel | Requires a lot of land, can contribute to deforestation |
| Sugarcane | 20-30 | 15,000 | High yield, can be grown in tropical climates | Requires a lot of water and fertilizer, can contribute to soil erosion |
The graph below shows the relationship between crop yield and environmental factors.

The model below predicts the energy output of different biofuel crops.

FAQ Compilation: Data Nugget Growing Energy Comparing Biofuel Crop Biomass
What factors influence the growth of biofuel crops?
Climate, soil conditions, water availability, and nutrient management are key factors that influence biofuel crop growth.
How does the energy content of biofuel crops vary?
The energy content of biofuel crops depends on the crop species, cultivation practices, and processing methods.
What are the challenges associated with biomass harvesting and processing?
Challenges include optimizing harvesting techniques, minimizing waste, and ensuring sustainable biomass management practices.