How much work did the movers do horizontally? This intriguing question sets the stage for an exploration into the multifaceted factors that influence the workload of movers as they navigate the horizontal plane. From calculating distance traveled to assessing load size and weight, this narrative delves into the intricacies of horizontal movement, providing a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and techniques involved.
As movers embark on their horizontal journey, they encounter a myriad of variables that shape their workload. The distance they traverse, the weight and size of the load they carry, and the terrain they navigate all play pivotal roles in determining the amount of work required.
This analysis will delve into each of these elements, unraveling their impact on the movers’ efforts.
Calculate Horizontal Distance Traveled
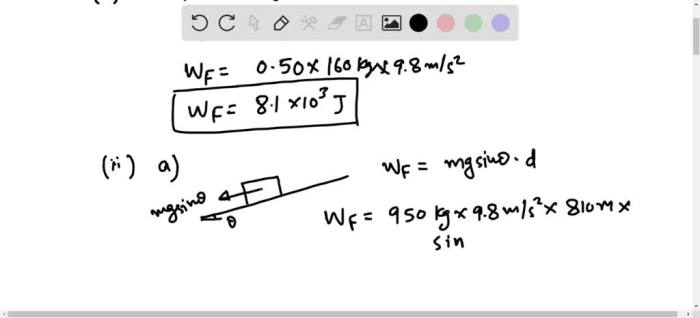
To determine the horizontal distance an object has moved, use the formula: Horizontal Distance = Final Horizontal Position – Initial Horizontal Position.
Measure the distance traveled horizontally using a measuring tape or laser level. Mark the initial and final positions of the object, then subtract the initial position from the final position to find the horizontal distance.
- Example 1: If an object moves from a horizontal position of 5 meters to a horizontal position of 10 meters, the horizontal distance traveled is 10 meters – 5 meters = 5 meters.
- Example 2: If an object moves from a horizontal position of -2 meters to a horizontal position of 3 meters, the horizontal distance traveled is 3 meters – (-2 meters) = 5 meters.
Assess Load Size and Weight
The amount of work done horizontally is influenced by the load size and weight.
- Load Size:Larger loads require more force to move horizontally than smaller loads.
- Load Weight:Heavier loads require more force to move horizontally than lighter loads.
Example: Moving a heavy sofa horizontally requires more effort than moving a light chair horizontally.
Analyze Moving Techniques and Equipment: How Much Work Did The Movers Do Horizontally

Different moving techniques and equipment can assist in horizontal movement.
Moving Techniques
- Dragging:Sliding the load across the surface.
- Lifting:Raising the load off the surface and carrying it.
- Rolling:Using wheels or rollers to move the load.
Equipment, How much work did the movers do horizontally
- Hand trucks:Two-wheeled carts for moving heavy loads.
- Dollies:Four-wheeled platforms for moving large loads.
- Lifting straps:Straps used to lift and carry heavy loads.
Example: Using a hand truck to move a heavy box horizontally reduces the effort required compared to dragging it.
Consider Obstacles and Terrain
Obstacles and terrain can impact horizontal movement.
Obstacles
- Walls:Obstacles that block horizontal movement.
- Furniture:Objects that can hinder horizontal movement.
- Stairs:Slopes that require additional effort to move horizontally.
Terrain
- Slopes:Inclined surfaces that increase the force required to move horizontally.
- Uneven surfaces:Surfaces with bumps or dips that make horizontal movement more difficult.
- Slippery surfaces:Surfaces with low friction that make horizontal movement less efficient.
Example: Moving a load horizontally through a narrow doorway requires maneuvering around the obstacle, increasing the effort required.
Estimate Time and Effort Required
Estimating the time and effort required for horizontal movement is crucial.
Time Estimation
- Distance:Longer distances require more time to cover horizontally.
- Load size and weight:Heavier and larger loads take longer to move horizontally.
- Obstacles and terrain:Obstacles and uneven terrain increase the time required for horizontal movement.
Effort Estimation
- Force:The amount of force required to move the load horizontally.
- Time:The duration of the horizontal movement.
- Power:The rate at which work is done horizontally.
Example: Moving a heavy load up a slope requires more effort and time compared to moving the same load on a flat surface.
Questions and Answers
What is the formula for calculating horizontal distance moved?
Horizontal distance = Square root of (Total distance traveled)^2 – (Vertical distance traveled)^2
How does load size impact horizontal movement?
Larger loads require more force to move, increasing the workload for movers.
What moving techniques can reduce horizontal workload?
Using dollies, ramps, and proper lifting techniques can minimize effort and strain.