Section 8.2 solubility and concentration – In the realm of chemistry, Section 8.2 delves into the intriguing concepts of solubility and concentration, shedding light on the behavior of substances in various environments. This discourse will unravel the intricate relationship between these two properties, exploring their practical applications in diverse fields.
Solubility, the extent to which a substance can dissolve in a solvent, is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent. Understanding these factors enables us to predict the solubility of substances and design solutions with desired concentrations.
Solubility
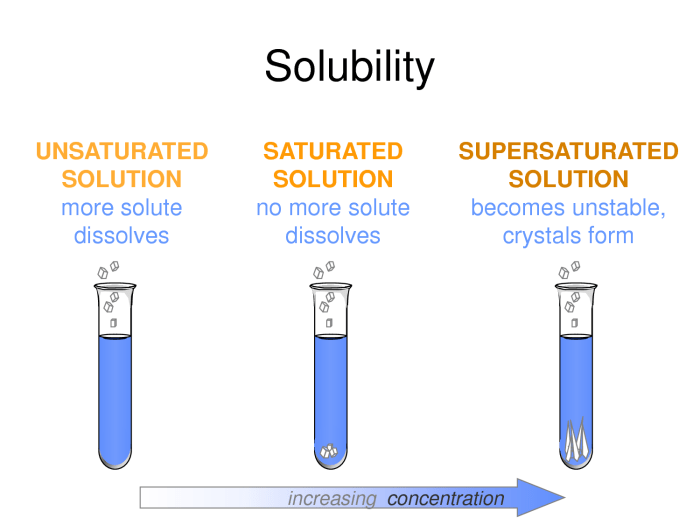
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture. The solubility of a substance is usually expressed in terms of its concentration, which is the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent.
Factors Affecting Solubility
- Temperature:The solubility of most solids increases with temperature, while the solubility of gases decreases with temperature.
- Pressure:The solubility of gases increases with pressure.
- Nature of solute and solvent:The solubility of a substance depends on the nature of both the solute and the solvent. Generally, polar solutes dissolve in polar solvents, while nonpolar solutes dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
Examples of Substances with High and Low Solubility
- High solubility:Sugar, salt, sodium chloride
- Low solubility:Oil, wax, gold
Concentration: Section 8.2 Solubility And Concentration

Concentration is a measure of the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent. It can be expressed in various units, including molarity (M), molality (m), and mass percentage (%).
Units of Concentration
- Molarity (M):Number of moles of solute per liter of solution
- Molality (m):Number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent
- Mass percentage (%):Mass of solute per 100 grams of solution
Calculating Concentration
The concentration of a solution can be calculated using the following formula:
Concentration = (Mass of solute / Molar mass of solute) / Volume of solution
Relationship between Solubility and Concentration
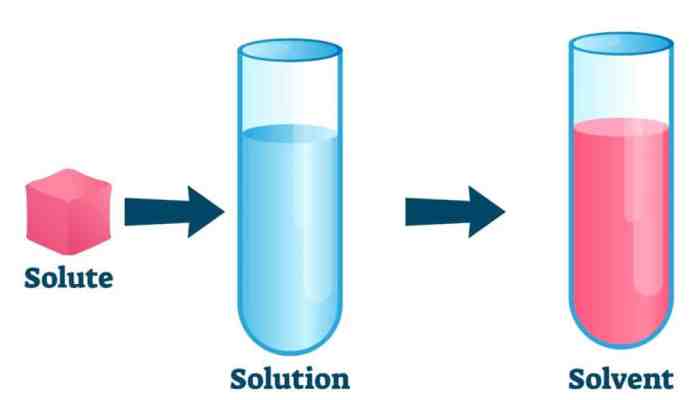
The solubility of a substance affects its concentration. The higher the solubility of a substance, the higher its concentration can be in a given solvent.
How Solubility Affects Concentration, Section 8.2 solubility and concentration
- If the solubility of a substance is high, it means that a large amount of solute can dissolve in a given amount of solvent, resulting in a high concentration.
- If the solubility of a substance is low, it means that only a small amount of solute can dissolve in a given amount of solvent, resulting in a low concentration.
Examples of Changes in Solubility Affecting Concentration
- Increasing temperature:For most solids, increasing temperature increases their solubility, leading to a higher concentration in solution.
- Decreasing pressure:For gases, decreasing pressure decreases their solubility, leading to a lower concentration in solution.
Applications of Solubility and Concentration

Solubility and concentration have numerous applications in everyday life and scientific research.
Applications of Solubility
- Household cleaning:Soaps and detergents dissolve in water to form solutions that can remove dirt and grime.
- Food preparation:Cooking involves dissolving ingredients in water or other solvents to create sauces, soups, and other dishes.
- Drug delivery:Medications are often dissolved in solvents to create solutions that can be administered orally or intravenously.
Applications of Concentration
- Chemical analysis:Concentration is used to determine the amount of a substance present in a solution.
- Medical diagnosis:Blood tests measure the concentration of various substances in the blood to diagnose and monitor health conditions.
- Environmental monitoring:Concentration is used to measure the levels of pollutants in air, water, and soil.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between solubility and concentration?
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given solvent under specific conditions, while concentration measures the amount of solute present in a given amount of solution.
How does temperature affect solubility?
Generally, the solubility of solids in liquids increases with increasing temperature, while the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with increasing temperature.
What is the relationship between solubility and concentration?
Solubility and concentration are directly proportional. As the solubility of a substance increases, the concentration of its solution also increases.

