Energy pyramids tying it all together – Energy pyramids, a fundamental concept in ecology, provide a concise and clear representation of the energy flow and trophic relationships within ecosystems. They offer insights into the dynamics of energy transfer, ecological roles of different organisms, and the impact of human activities on these intricate systems.
This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of energy pyramids, their limitations, and their applications in understanding ecosystem dynamics. By exploring the ecological roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness and stability of ecological communities.
Energy Pyramids: An Overview
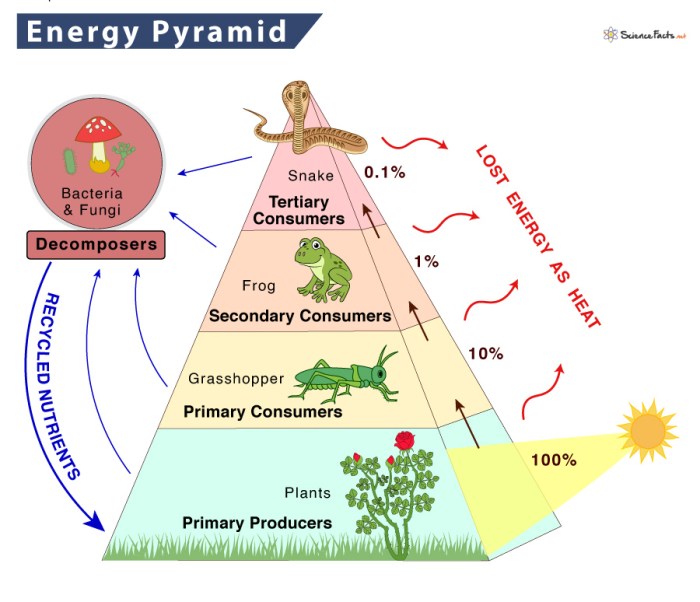
Energy pyramids represent the graphical depiction of energy flow through different trophic levels in an ecosystem. They illustrate the amount of energy available at each level and the efficiency of energy transfer. Energy pyramids are essential for understanding the structure and function of ecosystems.
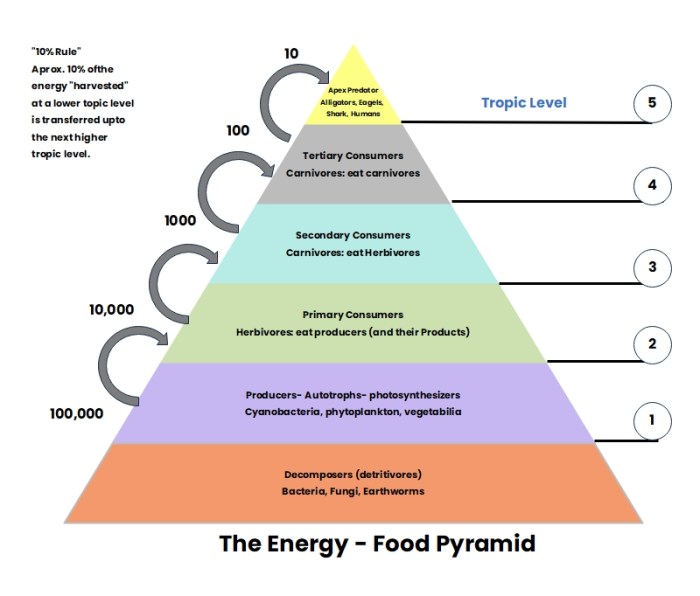
Energy pyramids are typically constructed with producers at the base, followed by primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. The width of each level represents the amount of energy available at that level. As energy flows through the pyramid, some is lost as heat, and the amount of energy available at each subsequent level decreases.
Energy pyramids are used to study ecosystem dynamics, predict the effects of environmental changes, and inform conservation planning and environmental management.
Energy Flow through Energy Pyramids
Energy flow through energy pyramids occurs through the transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next. Producers, such as plants, convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Primary consumers, such as herbivores, eat producers and use their energy for growth and reproduction.
Secondary consumers, such as carnivores, eat primary consumers and use their energy for the same purposes.
The efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels is typically around 10%. This means that only about 10% of the energy available at one level is transferred to the next level. The remaining energy is lost as heat.
Ecological Roles of Different Trophic Levels
The different trophic levels in an energy pyramid play specific ecological roles:
- Producers:Producers are the foundation of the food chain. They convert sunlight into chemical energy, which is used by all other organisms in the ecosystem.
- Consumers:Consumers are organisms that eat other organisms. Primary consumers eat producers, secondary consumers eat primary consumers, and so on. Consumers use the energy they obtain from their food for growth, reproduction, and other life processes.
- Decomposers:Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and organic matter. They release nutrients back into the ecosystem, which can be used by producers.
Biodiversity is important for maintaining the stability of energy pyramids. A diverse ecosystem has a variety of organisms at each trophic level, which helps to ensure that there is always a sufficient supply of food for all organisms.
Human Impact on Energy Pyramids, Energy pyramids tying it all together
Human activities can have a significant impact on energy pyramids. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can all disrupt energy flow and lead to the collapse of ecosystems.
- Pollution:Pollution can harm or kill organisms at all trophic levels. For example, pesticides can kill insects, which are important food sources for birds and other animals.
- Habitat destruction:Habitat destruction can reduce the amount of food available for organisms at all trophic levels. For example, deforestation can reduce the amount of food available for herbivores, which can lead to a decline in the populations of carnivores that eat them.
- Climate change:Climate change can alter the distribution of organisms and the availability of food. For example, rising temperatures can cause some species to move to new areas, which can disrupt the food chains in those areas.
Conservation and sustainable practices can help to protect energy pyramids and the ecosystems they support.
Applications of Energy Pyramids in Ecology
Energy pyramids are used to study ecosystem dynamics and predict the effects of environmental changes. For example, energy pyramids can be used to:
- Understand the flow of energy through ecosystems:Energy pyramids can show how energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. This information can be used to identify the most important organisms in an ecosystem and to understand how changes in one trophic level can affect the entire ecosystem.
- Predict the effects of environmental changes:Energy pyramids can be used to predict how changes in the environment, such as climate change or pollution, will affect the flow of energy through an ecosystem. This information can be used to develop strategies to mitigate the effects of these changes.
- Inform conservation planning and environmental management:Energy pyramids can be used to identify the most vulnerable species in an ecosystem and to develop strategies to protect them. This information can also be used to develop land use plans that minimize the impact on ecosystems.
FAQ Summary: Energy Pyramids Tying It All Together
What are the limitations of energy pyramids?
Energy pyramids assume a linear flow of energy, which may not always be the case in real ecosystems. Additionally, they do not account for energy losses due to respiration, decomposition, and other processes.
How can energy pyramids be used to study ecosystem dynamics?
Energy pyramids provide a snapshot of the energy distribution within an ecosystem at a given time. By comparing energy pyramids of different ecosystems or over time, researchers can gain insights into changes in energy flow patterns and ecosystem productivity.